Table of contents
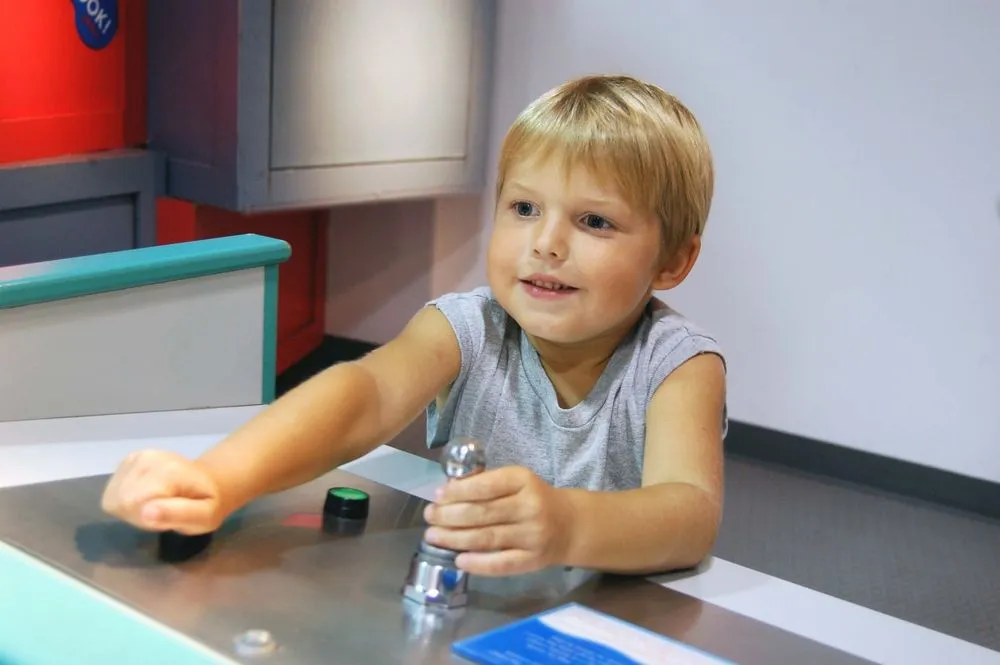
The benefits of interactive museums and exhibits cannot be disputed and that is why they are becoming more popular. These museums let people touch and use the exhibits, which is more fun than just looking at them. They also use technology to make the exhibits more interesting.
A survey found that
75% of people
who go to museums like the interactive exhibits the best. This is because they can learn about history, science, and art in a fun way. For example, an exhibit that uses virtual reality can take people back in time to see what life was like.
Interactive museums are also good for education. Studies have shown that they can help children learn critical thinking skills, teamwork, and communication. They can also help people who have trouble learning in traditional ways.
An article in Discover Magazine said that interactive exhibits help children learn better. It also said that people like to learn by doing, not just by listening.
Interactive exhibits are a great way to learn. As technology gets better, we will see even more interactive exhibits in museums.
The Benefits of Interactive Exhibits

Museums are using interactive exhibits more and more to make their visitors learn and have fun. These exhibits can be touched and played with, which helps people learn better. They can also be very interesting and make people want to learn more. Here are some of the benefits of interactive exhibits:
1. Learning Opportunities
Interactive exhibits offer visitors a unique opportunity to learn by doing. Unlike traditional museum displays, which are often static and passive, interactive exhibits allow visitors to experiment, observe, and make discoveries for themselves. This active engagement with the content leads to deeper learning and retention of information.
A study by the
Association of Science-Technology Centers
found that visitors who engaged in interactive exhibits retained more information than those who only observed. This is especially true for children, who benefit greatly from hands-on learning experiences. When children are able to touch, feel, and manipulate objects, they are better able to understand and remember the concepts being presented.
For example, a child visiting a science museum might be able to experiment with different levers to see how they work. This hands-on experience would help the child to understand the concept of leverage in a way that they would not be able to from simply reading about it.
Interactive exhibits can also be used to promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By presenting visitors with a challenge or puzzle, interactive exhibits can encourage them to think creatively and come up with their own solutions. This type of active learning is essential for developing the skills that students need to succeed in school and in life.
2. Engagement and Active Learning

Interactive exhibits are more engaging than passive exhibits because they allow visitors to participate in the learning process. This active participation helps visitors to better understand the subject matter.
For example, a passive exhibit about the solar system might simply display a model of the solar system. A visitor might look at the model and read the labels, but they would not have a very deep understanding of how the solar system works.
An interactive exhibit about the solar system, on the other hand, might allow visitors to manipulate objects, such as the planets and the sun. Visitors could also solve puzzles to learn more about the solar system. This active participation would help visitors to develop a better understanding of how the solar system works.
In addition to leading to better understanding, active participation also leads to better retention. When visitors are actively engaged in the learning process, they are more likely to remember what they have learned.
This is because active participation helps to create a stronger connection between the learner and the material being learned. When visitors manipulate objects or solve puzzles, they are creating a mental model of the subject matter. This mental model helps them to remember what they have learned even after they have left the exhibit.
Overall, interactive exhibits are more engaging and lead to better retention than passive exhibits. This is because interactive exhibits allow visitors to participate in the learning process and create a stronger connection between themselves and the material being learned.
3. Multi-Sensory Experience
Interactive exhibits are fun and educational. They use pictures, sounds, touch, and even smells to make learning interesting. This helps people remember what they learn better.
Visual components, like pictures and videos, help people see what they are learning about. This can help people understand things better, especially if they learn in different ways.
Auditory cues, like narrations, music, and sounds, help people hear what they are learning about. This can help people feel like they are part of the experience and can make learning more exciting.
Tactile components, like touchscreens and objects, help people touch what they are learning about. This can help people learn by doing and can make learning more hands-on.
Olfactory components, like smells, can help people smell what they are learning about. This can help people feel like they are really there and can make learning more immersive.
All of these sensory experiences together make learning more fun and memorable. Interactive exhibits are a great way to learn about new things and to remember what you have learned.
4. Personalised Learning

Personalized learning is an educational approach that tailors the learning experience to each individual learner. This can be done by providing different learning activities, resources, and assessments that are appropriate for the learner’s needs, interests, and learning style.
Interactive exhibits are a great way to provide personalized learning because they offer a variety of activities that can be explored at the learner’s own pace. For example, a learner who is interested in animals might choose to watch a video about a specific animal, while a learner who is more interested in learning about the history of the exhibit might choose to read a text panel.
The flexibility of interactive exhibits allows for both casual learners and those seeking in-depth knowledge to have a personalized learning experience. Casual learners can simply explore the exhibit at their own pace and focus on the activities that interest them the most. Those seeking in-depth knowledge can take the time to read all of the text panels and watch all of the videos.
5. Fostering Curiosity and Critical Thinking
Museum exhibits can be more than just places to look at things. Interactive exhibits can help people learn by making them curious and helping them think critically.
When people interact with an exhibit, they start to ask questions. They want to know how things work and why they are the way they are. This curiosity leads to learning.
Interactive exhibits also help people think critically. They have to figure out how things work and solve problems. This helps them understand complex concepts and make good decisions.
Interactive exhibits can be fun and exciting. They can help people learn in a way that is memorable and engaging. They can also help people develop skills that they can use in the real world.
6. Enhancing Collaboration and Social Interaction

Interactive exhibits are different from regular exhibits because they let people work together. They are good for friends, families, and school groups because they let people share their ideas and work together to solve problems. This makes people learn better and have more fun.
The benefits of collaboration go beyond the exhibit. People learn about different viewpoints and become more understanding. They also feel like they are part of a community. This makes learning more interesting and helps people remember what they learn.
Interactive exhibits are a great way to learn and have fun. They are more than just exhibits, they are experiences.
7. Technology Integration
Museums are using technology to make exhibits more interactive and engaging. They are using touchscreens, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) to let visitors learn in new and exciting ways.
Touchscreens let visitors access information about exhibits with just a tap. AR overlays digital images onto the real world, so visitors can see historical scenes come to life. VR lets visitors explore different places and times, like walking through ancient Rome or flying over the Grand Canyon.
These new technologies are making museums more appealing to people of all ages. They are also helping museums teach people about the world in new and interesting ways. Museums are no longer just places to look at old things. They are places where people can learn and explore.
8. Memorable Experiences

Interactive exhibits create memorable experiences that visitors are likely to remember long after their museum visit. These experiences inspire curiosity and excitement, making visitors eager to learn more. According to a
study
, visitors who engage in interactive exhibits are more likely to return to the museum and recommend it to others.
Interactive exhibits also provide opportunities for visitors to engage with historical and cultural content in new and exciting ways. For example, visitors can use technology like virtual reality and augmented reality to explore historical sites and artifacts. This immersive experience can create a deeper understanding and appreciation of history and culture.
Examples of Interactive Exhibits
Here are a few examples of interactive exhibits that museums have used to engage visitors:
i. Touchscreens
Touchscreens have become a ubiquitous feature in modern museums, revolutionising the way visitors engage with content. Museums leverage touchscreens to offer a rich array of digital experiences. For instance, visitors can embark on virtual tours that transport them to far-off locations and historical periods. With a simple touch, intricate details of artefacts, artworks, and historical objects are at their fingertips, accompanied by comprehensive explanations and context. These touchscreens also serve as gateways to interactive games that challenge visitors to solve puzzles, answer questions, and learn through play. The tactile interaction with touchscreens makes information accessible and engaging, making learning an enjoyable and immersive endeavour.
ii. Hands-on Exhibits
Hands-on exhibits have breathed new life into the museum experience by shifting from passive observation to active participation. These exhibits encourage visitors to explore with their sense of touch, fostering a deeper connection to the subject matter. Whether it’s a replica of an ancient tool, a puzzle representing a scientific concept, or a texture station offering tactile exploration of materials, hands-on exhibits invite experimentation and observation. Visitors can manipulate objects, understand their functionality, and gain insights through trial and error. This approach is particularly beneficial for younger visitors, as it ignites curiosity and enhances learning through sensory engagement.
iii. Interactive Displays

Interactive displays represent a fusion of art and technology, transforming static exhibits into dynamic experiences. These displays incorporate cutting-edge technology such as sensors, motion detection, and projections to create immersive environments that respond to visitors’ movements and actions. For instance, visitors might stand before a large screen depicting a historical scene. As they move, the scene unfolds, revealing different perspectives and layers of information. These displays encourage visitors to explore, triggering animations, changing visual perspectives, and revealing hidden details. The synergy between technology and content adds an element of surprise and discovery, making museum visits memorable and captivating.
iv. Paintings and Art Exhibits
The marriage of traditional art and interactive technology has given rise to a new dimension of artistic appreciation within museums. Interactive technology enriches visitors’ experiences with paintings and art exhibits by providing additional layers of information and context. As visitors approach a masterpiece, interactive screens can offer insights into the artist’s life, the historical period, and the techniques employed. Magnifying specific portions of a painting on a screen allows viewers to discern intricate details that might otherwise go unnoticed. Moreover, interactive displays can allow visitors to virtually restore deteriorated artworks, offering a glimpse into the past and the meticulous processes of preservation. This integration of technology redefines the way art is perceived, making it a multi-dimensional exploration that bridges the gap between the past and the present.
Incorporating touchscreens, hands-on exhibits, interactive displays, and technology-enhanced art experiences into museums has reimagined the way visitors interact with content. These interactive elements foster engagement, encourage exploration, and provide a holistic and immersive learning experience that caters to a diverse range of interests and learning styles.
The Importance of Interactivity in Museum Experiences
Interactive museums and exhibits have become increasingly popular in recent years. This is due to the many benefits they offer in terms of education, engagement, and entertainment. In this section, we will explore the importance of interactivity in museum experiences and how it can enhance visitors’ connections with exhibits.
(a) Connecting with Visitors

One of the primary benefits of interactive exhibits is that they provide visitors with a more personal and engaging experience. By allowing visitors to interact with exhibits in a hands-on way, they can create a deeper connection with the subject matter. This connection can lead to increased interest and understanding of the topic.
According to a
study
, interactive exhibits are more effective at engaging visitors than traditional static displays. The study found that visitors spent an average of 30% more time at interactive exhibits and were more likely to remember the information presented.
(b) Teaching through Emotion
Another benefit of interactive exhibits is that they can teach through emotion. By creating an emotional connection with visitors, exhibits can be more effective at conveying complex ideas and concepts. For example, an exhibit about climate change may be more impactful if visitors can experience the effects of rising sea levels through a virtual reality simulation.
Interactive exhibits can also be used to teach empathy and understanding. For example, an exhibit about the refugee crisis may include interactive elements that allow visitors to experience living in a refugee camp. This can help visitors develop a deeper understanding and empathy for those affected by the crisis.
(c) Scale and Imagination
Interactive exhibits can also provide visitors with a sense of scale and imagination. By allowing visitors to interact with exhibits in a three-dimensional space, they can get a better sense of the size and scope of the topic. This can be particularly effective for exhibits about space, architecture, or natural history.
Finally, interactive exhibits can encourage creativity and exploration. By allowing visitors to interact with exhibits in a non-linear way, they can explore and discover new things on their own terms. This can be particularly effective for exhibits aimed at children and youth.
In conclusion, interactivity is an essential component of modern museum experiences. By providing visitors with a more personal and engaging experience, interactive exhibits can enhance visitors’ connections with exhibits and increase their understanding and retention of information. Whether it’s through emotional connections, scale, and imagination, or creativity and exploration, interactive exhibits offer a unique and valuable experience for visitors of all ages.